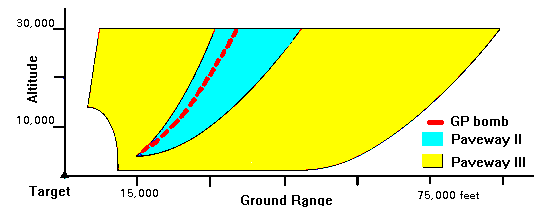


Unlike the Paveway II LGB, the LLLGB can correct for relatively large deviations from planned release parameters in the primary delivery mode (low-altitude level delivery). It also has a larger delivery envelope for the dive, glide and loft modes than does the earlier LGB. The wide field of view and midcourse guidance modes programmed in the LLLGB allow for a "Point Shoot" delivery capability. This capability allows the pilot to attack the target by pointing the aircraft at the target and releasing the weapon after obtaining appropriate sight indications. The primary advantage of this capability is that accurate dive/tracking is not required to solve wind drift problems.
In the Gulf War all of the 1,181 GBU-24s were released by F-111Fs.In 1996 the Navy conducted tests of the F-14A Tomcat with the GBU-24B/B Hard Target Penetrator Laser-Guided Bomb at Naval Air Station Patuxent River, Md., as part of an air-to-ground development program to support clearance for use of the weapon in the fleet by F-14 Tomcats.
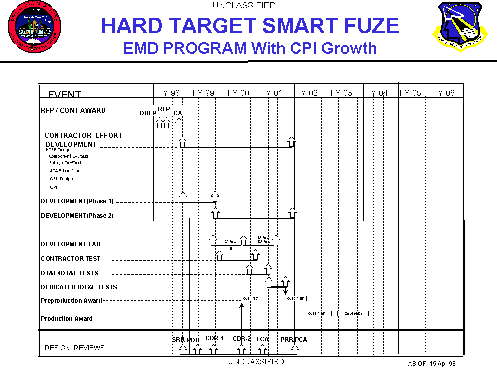
Key accomplishments in 1996 included demonstration of controlled weapon penetration and detonation depth using the Hard-Target Smart Fuse [HTSF] and successful integration of the GBU- 24/ HTSF with F-15E and F/A- 18 aircraft. The Hard-Target Smart Fuse, developed at the Wright lab, features an accelerometer that can be programmed to detonate the bomb at a precisely specified depth significantly enhancing munition lethality. The Defense Special Weapons Agency (DSWA) Counterproliferation Initiative (CPI) requires development, integration and certification of HTSF with GBU-24 B/B (Navy BLU-109) and GBU-24 D/B (Navy BLU-116) under this effort. Under a separate effort, CPI will integrate the GBU-24 B/B and GBU-24 D/B configuration HTSFs into the CPI modified Conventional Air Launched Cruise Missile (CALCM) and Tactical Land Attack Missile (TLAM) weapons.
The Multi-Segment Hard Target Penetrator (MSHTP) concept has been designed to use the penetration capability of a BLU-113 or BLU-109 linked to the void counting hard target smart fuse. This weapon detonates a copper cutter charge upon entering the target and cuts the rear portion of the bomb off, which then detonates. The rest of the weapon continues down to the next level.
The Advanced Unitary Penetrator [AUP] hard target penetrator features an elongated narrow diameter case made of a tough nickel-cobalt steel alloy called Air Force 1410. With the official designation of BLU-116, and designated the GBU-24 C/B (USAF) and GBU-24 D/B (Navy), is designed to provide at least twice the penetration capability of existing BLU-109 2000-pound bombs. The AUP is being demonstrated with Boeing as prime and Lockheed-Martin as subcontractor. Penetration capability is directly proportional to the warhead's sectional density--its weight divided by its cross section. The AUP maximizes sectional density by reducing the explosive payload and using heavy metals in the warhead case. Lower explosive payload will diminish dispersion of NBC agents to help reduce collateral effects. The AUP will retain the carriage and flight characteristics of the BLU-109, and it will be compatible with the GBU-24, GBU-27, and GBU-15/AGM-130 series of precision-guided bombs. Thus, the AUP will be capable of delivery from a wider inventory of aircraft, including stealth platforms, than the BLU-113/GBU-28. A proposal to replace the current CALCM warhead with an AUP warhead provides 2.5 times BLU-109 penetration capability.
The AUP development effort was conducted in support of the Counterproliferation Initiative (CPI) Advanced Concept Technology Demonstration (ACTD). The program objective was to develop and demonstrate a weapon that could be rapidly transitioned for Air Force and Navy use against hardened targets associated with the production, storage, and weaponization of chemical or biological agents. Normally, the introduction of a new weapon is a very long, expensive, and tedious process - as long as ten years or more. The associated cost may be tens of millions of dollars.
The 1700-pound AUP warhead is tucked inside a lightweight aerodynamic shroud. This "outer skin" gives the AUP the exact physical and aerodynamic characteristics of the BLU-109. The shroud strips away from the internal penetrator when the weapon impacts the target. Compared to the BLU-109, the AUP has thicker case walls, a tougher case material, an improved nose shape, and a smaller explosive charge. The cross-sectional area of the AUP penetrator, however, is only half as great as the cross-sectional area of the BLU-109. A smaller explosive charge reduces collateral damage potential by reducing blast overpressure that could expel chemical or biological agents from the target. A long testing series demonstrated AUP's compatibility with the Munitions Directorate-developed Hard Target Smart Fuze (HTSF). The HTSF allows the AUP to be detonated at the optimal point within a target to inflict maximum damage. That ability compensates for the reduction in explosive charge.
Because it's a "twin" to the BLU-109, the AUP can utilize a proven system of hardbacks, guidance units, and tail fin kits. The costs associated with developing new kits is eliminated. The operational users - pilots, weapon handlers and load crews - will gain the improved war fighting capabilities of the AUP without the costs associated with retraining support personnel or the acquisition of new delivery systems and support equipment. Battle commanders will also have increased ability to neutralize deeply buried hardened targets.
GBU-24 E/B
GBU-24E/B, an Enhanced Paveway Laser Guided Bomb, is a precision-guided hardened target penetrator used to destroy hardened aircraft hangers and underground bunkers. It integrates a Global Positioning System and a ring laser gyro inertial measuring unit (IMU) to the already fielded GBU-24B/B "Paveway III" with the existing laser guidance. A new guidance and control unit has been modified to incorporate GPS electronics, GPS antenna, IMU and software for precision GPS/INS guidance. Testing of this system began in late 1999.
Specifications | |
| Mission | Close air support, interdiction, offensive counter air, naval anti- surface warfare |
| Targets | Mobile hard, fixed soft, fixed hard |
| Service | Air Force, Navy |
| Program status | Operational |
| First capability | 1983 |
| Guidance method | Laser (man-in-the-loop) |
| Range | Greater than 10 nautical miles |
| Development cost | Not available - Air Force officials stated that development cost was not available because they do not have records covering the development period. |
| Production cost | $729.138 million |
| Total acquisition cost | Not available |
| Acquisition unit cost | Not available |
| Production unit cost | $55,600 |
| Quantity | 13,114 |
| Platforms |
A-6 A-10 F-14 F-15 F-16 F/A-18 F-111 |