
 10,000-pound
external load, and deploying 2,100 nautical miles with a single aerial
refueling. The MV-22's rotor system and engine/transmission nacelle mounted
on each wingtip allow it to operate as a helicopter for takeoff and landing.
Once airborne, the nacelles rotate forward 90 degrees, converting the MV-22
into a high altitude, fuel-efficient turboprop aircraft.
10,000-pound
external load, and deploying 2,100 nautical miles with a single aerial
refueling. The MV-22's rotor system and engine/transmission nacelle mounted
on each wingtip allow it to operate as a helicopter for takeoff and landing.
Once airborne, the nacelles rotate forward 90 degrees, converting the MV-22
into a high altitude, fuel-efficient turboprop aircraft.
The program is currently in the Engineering and Manufacturing Development phase. The aircraft has completed Operational Assessment IIB, high/hot hover performance trials, and has accrued over 1,100 flight hours with the Full Scale Development and E&MD aircraft. The Osprey enters the Developmental Test/Operational Test phase in 1997; aircraft deliveries to operating forces begin in 1999 and initial operational capability is scheduled for 2001.
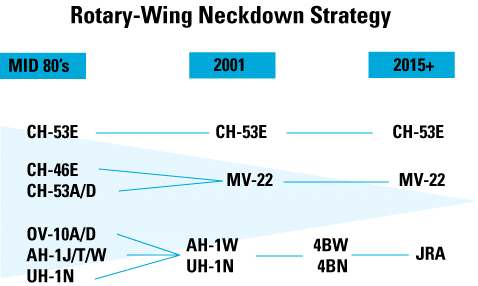
The H-1 Upgrade program replaces the current two-bladed rotor systems on the UH-1N and AH-1W aircraft with a new, four-bladed, all-composite rotor system coupled with a sophisticated, fully integrated cockpit and state-of-the-art technical enhancements. This 4BN/4BW remanufacture program reduces life-cycle costs, significantly improves operational capabilities, resolves existing safety deficiencies, and extends the service lives of both aircraft. Commonality between aircraft greatly enhances the maintainability and deployability of the systems with both aircraft supported and operated within the same squadron structure.
 The CH-46E Sea Knight
helicopter is a day/night assault transport of combat troops, supplies,
and equipment during amphibious landings and subsequent operations ashore.
Additional tasks are evacuation operations and other maritime special operations;
over-water search and rescue augmentation; support for mobile forward refueling
and rearming points; and aeromedical evacuation of casualties from the
field.
The CH-46E Sea Knight
helicopter is a day/night assault transport of combat troops, supplies,
and equipment during amphibious landings and subsequent operations ashore.
Additional tasks are evacuation operations and other maritime special operations;
over-water search and rescue augmentation; support for mobile forward refueling
and rearming points; and aeromedical evacuation of casualties from the
field.
Normal airframe operational and attrition rates have taken the CH-46 force to the point where a medium lift replacement is required. Several safety and capability upgrades - interim measures to allow continued safe and effective operation of the Sea Knight fleet until its replacement by the MV-22 - are currently in work, including: a dynamic component upgrade, a communication/navigation control system, Night Vision Goggle Head-Up Display (NVG HUD), GPS, and AN/ARC-210 radios.
 A more capable version
of the CH-53A introduced into the Marine Corps in 1966, the CH-53D Sea
Stallion is designed to transport equipment, supplies, and personnel during
the assault phase of an amphibious operation and subsequent operations
ashore. Capable of carrying supplies both internally and externally, the
CH-53D is shipboard compatible and capable of operation in adverse weather
conditions both day and night. It can carry 37 passengers in its normal
configuration and 55 passengers with centerline seats installed.
A more capable version
of the CH-53A introduced into the Marine Corps in 1966, the CH-53D Sea
Stallion is designed to transport equipment, supplies, and personnel during
the assault phase of an amphibious operation and subsequent operations
ashore. Capable of carrying supplies both internally and externally, the
CH-53D is shipboard compatible and capable of operation in adverse weather
conditions both day and night. It can carry 37 passengers in its normal
configuration and 55 passengers with centerline seats installed.
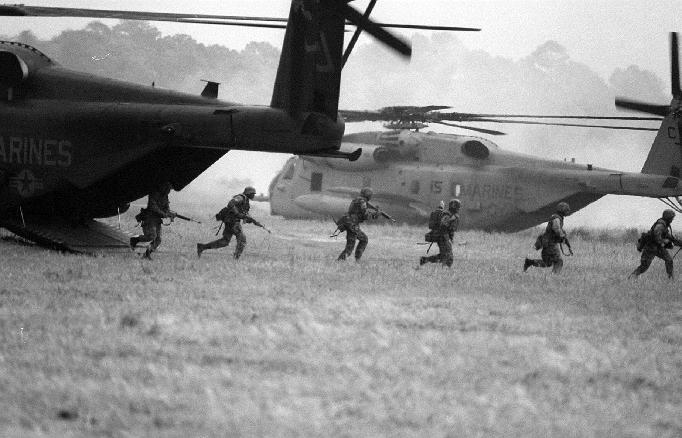 The CH-53E is the
Marine Corps heavy-lift helicopter. The aircraft is capable of lifting
16 tons at sea level, transporting the load 50 nautical miles, and returning.
The CH-53E can be refueled in flight, giving the helicopter a virtually
indefinite range. The aircraft is compatible with most amphibious warships.
It seats 37 passengers in its normal configuration and has provisions to
carry 55 passengers with centerline seats installed. The CH-53E Super Stallion
provides the MAGTF the capability to deliver heavy and outsized cargo,
artillery, and light armor vehicles. It also provides a rapid combat resupply
opportunity when needed. Funded operational safety improvement programs
for the aircraft include GPS, AN/ARC-210 radios, and NVG HUD.
The CH-53E is the
Marine Corps heavy-lift helicopter. The aircraft is capable of lifting
16 tons at sea level, transporting the load 50 nautical miles, and returning.
The CH-53E can be refueled in flight, giving the helicopter a virtually
indefinite range. The aircraft is compatible with most amphibious warships.
It seats 37 passengers in its normal configuration and has provisions to
carry 55 passengers with centerline seats installed. The CH-53E Super Stallion
provides the MAGTF the capability to deliver heavy and outsized cargo,
artillery, and light armor vehicles. It also provides a rapid combat resupply
opportunity when needed. Funded operational safety improvement programs
for the aircraft include GPS, AN/ARC-210 radios, and NVG HUD.