MINE WARFARE PROGRAMS
Mine warfare concepts under development underscore the Navy’s goal to provide effective,
proactive mine countermeasures (MCM) to avoid or eliminate the mine threat during all phases of
forward-deployed operations. The application of MCM capabilities throughout the operating forces
is fundamental to ensuring that the mine threat can be neutralized. Mine operations will include a
synergistic use of intelligence, strategic mapping and surveillance, tactical surveillance and
reconnaissance, self-protection initiatives organic to non-MCM forces, and dedicated mine
countermeasures forces to clear unavoidable mines and mine fields. As recognized by the
Institute for Defense Analysis in late 1997, mining is also a force multiplier in today’s and
tomorrow’s conflict scenarios, and proposals are being addressed to enhance the Navy’s mining
capabilities. Some of the key programs that support the Navy’s mine warfare vision are discussed
in this section.
Dedicated Mine Countermeasure Systems
SQQ-32
Advanced Surface Mine-hunting Sonar
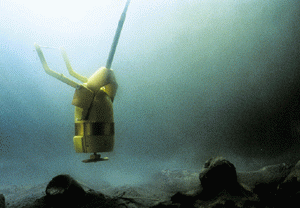
Description: The AN/SQQ-32 is a variable-depth mine-hunting detection and classification sonar for the Avenger (MCM-1) and Osprey (MHC-51) surface mine countermeasures (SMCM) ships. Its detection and classification capabilities are significantly improved compared to earlier sonars. The system provides for increases in operating depth, range, coverage rates and a greatly enhanced probability of detection on a single pass. Additionally, AN/SQQ-32 independently displays search and classification information using separate classification transducers in a stabilized, variable depth body. With near-photographic quality resolution, the SQQ-32 has
unprecedented capability to discriminate between actual mines and mine-like contacts. This
dramatically decreases false target reporting and increases classification reliability. Its multi-beam
operation increases the system’s search rate and can operate in shallow water.
Program Status: Milestone III was achieved in the fourth quarter FY 1994. Installation on all new-construction MHC-51 ships is complete. The phased-replacement for the AN/SQQ-30 sonars on MCMs is complete except for MCM-2 and MCM-8. These are scheduled to complete by the end of FY 2000.
Developer/Manufacturer: Raytheon/Thomson CSF, Portsmouth, Rhode Island.
VSW MCM
Very Shallow Water Detachment
Description: Adversary naval mines will continue to challenge the Navy and Marine Corps’ Forward...From the Sea strategic and related operational concepts in future crises and conflicts. In recognition of this asymmetrical threat to U.S. naval operations, the Navy successfully
completed a feasibility demonstration with the Very Shallow Water (VSW) MCM Test Detachment
during 1997 and 1998. The Chief of Naval Operations subsequently authorized the establishment
of a permanent VSW MCM Detachment under the Commander, Mine Warfare Command,
Ingleside, Texas. This detachment, which is in the process of transitioning from its prototype state
to an operational unit, with an Initial Operational Capability in FY 2000, will provide a capability for
conducting advanced-force and pre-assault MCM exploratory and reconnaissance operations in
the VSW zone (from 10- to 40-foot water depths) to locate and, if required, to clear potential
landing sites in support of joint littoral power-projections operations.

The VSW MCM Detachment, comprising Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD), Naval Special
Warfare (NSW/SEAL), and Marine Corps Force Reconnaissance divers, as well as marine
mammals, is responsible for developing tactics, techniques, and procedures for MCM operations
in the VSW zone and with achieving a capability to mobilize rapidly and to embark with deployed
amphibious task groups during contingencies. When not deployed, the VSW MCM Det will be the
Navy’s VSW warfighting laboratory for evaluating prototype systems that offer capability
improvements in this complex and critically important naval warfare area.
Program Status: Abbreviated acquisition programs are ongoing to acquire a diver-held Integrated Navigation Sensor System (INSS) that will provide divers in the VSW zone a visually enhanced sensor and a precise navigation capability with a single, small unit. This, coupled with a VSW
Underwater Breathing Apparatus (UBA) also in development under an abbreviated acquisition
program, will enable a first-ever minefield-suitable capability for detection and reacquisition of
mines in the VSW zone. Additionally, the Ex-8 Marine Mammal System (MMS) acquisition
program began in early FY 1998 to train, test, and evaluate existing Navy Atlantic and Pacific
bottlenose dolphins to work closely with the VSW MCM Det’s people, as well as to merge
prototype capabilities with new technology to stand up an operational MMS/VSW MCM Det.
Concepts of operations for integrated ARG support are also being developed.
Developer/Manufacturer: Ex-8 MMS: Naval Space and Electronic Warfare Systems Center (formerly NRaD) in San Diego, California. INSS/UBA developers: To be determined.
Naval Mining
ISLMM
Improved Submarine-Launched Mobile Mine
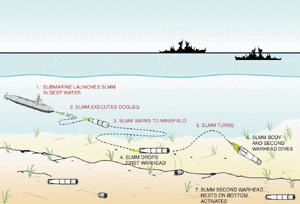
Description: The in-service Mk 67 SLMM, the Navy’s sole submarine-launched, multi-purpose (anti-submarine and -surface) mobile mine is increasingly obsolescent and is being phased out of the inventory. Based on an early 1960s-era Mk 37 torpedo, the weapon’s stand-off distance and placement accuracy are inadequate for many littoral warfare missions, its capability to detect many key targets is in doubt, and it is becoming increasingly costly to maintain. However,
because of the significant “force-multiplier” value of naval mines, the Navy has decided to pursue
an innovative modification of early variants of the Mk 48 heavyweight torpedo to an Improved
SLMM configuration. A joint effort between the United States Navy and the Royal Australian
Navy, ISLMM will enable the clandestine capability to plant minefields from a safe standoff
distance throughout the world’s littoral regions, to interdict military and hostile commercial traffic,
and thereby support sea control and battlespace dominance needs. ISLMM characteristics offer
increased range and precision placement accuracy, course-change capabilities, low-cost
maintenance, and greater loadout for the delivery submarine. Armed with two warheads, each
ISLMM will be able to attack two separate targets. The Mk 48-based delivery vehicle will be
compatible with all current and future submarine torpedo rooms and tubes.
Program Status: The ISLMM Cooperative Project will enter a three-year Engineering and
Manufacturing Development Phase beginning in FY 2000 followed by a three-year procurement
phase beginning in FY 2002.
Developer/Manufacturer: To be determined.
Naval Mines
Description: The Navy’s mine research and development programs are focusing on the need to improve the effectiveness of U.S. naval mines in joint expeditionary warfare scenarios. The
current Quick Strike (QS) family of bottom mines though very capable, will be enhanced by
incorporating the Target Detecting Device (TDD) Mk 71, which reached Milestone III in 1995, and
provides advanced mine algorithms for ship detection, classification, and localization against
some of the emerging threats (i.e., quiet diesel-electric submarines, mini-subs, fast patrol boats,
air cushioned vehicles).
In future years, exploratory research will pursue multi-influence (acoustic, magnetic, pressure,
seismic) sensors, data fusion of multiple influences, advanced sensors for bottom-mine
applications, and mid-water depth mine concept evaluation. Engineering development efforts
include advanced mine algorithms for ship detection, classification, and localization; development
of a remote control for mines (RECO) program; and concept evaluation and requirements
generation for the next-generation naval mine — the Littoral Sea Mine (LSM). Engineering
development has commenced for an Improved Submarine-Launched Mobile Mine (ISLMM), to
replace the obsolescent Mk 67 SLMM. ISLMM is a Cooperative Development Program of the
U.S. Navy and the Royal Australian Navy to provide for an enhanced covert stand-off mining
capability (see separate program summary for ISLMM).
Program Status: RECO and LSM programs are scheduled to begin research and development in FY 2000 and FY 2001, respectively. Procurement of TDD Mk 71 is scheduled to begin in FY 2001.
Developer/Manufacturer: To be determined.
Organic Mine Countermeasure Systems
AMNS
Airborne Mine Neutralization System
Description: The Airborne Mine Neutralization System (AMNS) is an expendable, remotely operated mine neutralization device, deployed from H-60 helicopters that will be capable of
providing identification and neutralization of proud (unburied) and close-tethered mines. AMNS
will be sent to the detected mine location where it will deploy its neutralization device to reacquire
and neutralize previously identified targets. The AMNS will be fully integrated into the H-60
avionics architecture.
Program Status: AMNS is in the Engineering and Manufacturing Development phase, leveraging Non-Developmental Items and Commercial-off-the-Shelf technologies. A competitive contract
was awarded December 1998 for the integration and testing of a COTS/NDI device from a MH-
53E helicopter. Integration into the H-60 will continue through FY 2003. Milestone III is projected
for third quarter FY 2003.
Developer/Manufacturer: Lockheed Martin, Nashau, New Hampshire; STN Atlas, Germany.
Assault Breaching Programs

Description: The Assault Breaching Programs encompass several projects planned to counter the threat to amphibious forces from known and projected land and naval mines and obstacles in shallow water, very shallow water, and surf zone approaches to amphibious operating areas. It
also includes craft landing zones ashore for amphibious assault craft and air-cushioned vehicles.
Systems being developed for mine sweeping, explosive clearance, and marking in this
challenging environment include Shallow-Water Influence Minesweep System (SWIMS), Shallow-
Water Assault Breaching (SABRE) system, Distributed Explosive Technology (DET), and the
Explosive Neutralization Pre-Planned Product Improvement (ENP3I) Program.
SABRE is a rocket-launched explosive line charge launched from a Landing Craft Air Cushion
(LCAC) vehicle, designed to clear assault lanes in the 10-foot to three-foot region of the surf
zone. DET is a rocket-launched explosive net, also launched from an LCAC, designed to clear
the remainder of the lanes in the three-foot to shore region of the surf zone. The EN program is a
pre-planned product improvement to SABRE and DET. It will provide increased LCAC
survivability and system accuracy through development of a fire control system, LCAC autopilot,
and extended-range rockets.
Program Status: SABRE and DET are basic explosive systems designed to operate together to meet near-term operational requirements, and are scheduled to be fielded beginning in FY 2001. Production of the ENP3I improvements to SABRE and DET will begin in FY 2004.
Developer/Manufacturer: To be determined.
Magic Lantern
Deployment Contingency System

Description: The lead development program is the Airborne Laser Mine Detection System (ALMDS), an electro-optical mine detection system that uses an aircraft-mounted laser to detect floating and keel-depth moored mines. The capability was successfully demonstrated during an
operational assessment in 1995. FY 1996 and FY 1997 efforts included the integration of the
Advance Development Models in the SH-2G LAMPS Mk I helicopters (previous efforts were
conducted using an SH-2F) to provide an interim contingency capability in the Naval Reserve
Force, with the goal of eventually integrating ALMDS in the active-duty H-60 helicopter force.
Program Status: Three contingency systems are operational with Light Anti-Submarine Helicopter Squadron 94 (HSL-94), Willow Grove, Pennsylvania.
Developer/Manufacturer: Contingency systems: Kaman Corporation, Bloomfield, Connecticut. Production Systems: To be determined.
RMS
Remote Mine-hunting System
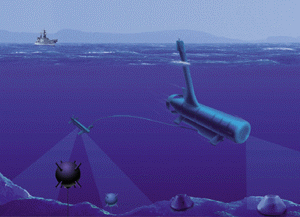
Description: To sustain operations in the littorals, naval forces must possess an organic capability to assess the extent of the naval mine threat. As part of the advanced forces, surface ships will employ off-board systems to meet the demand for mine reconnaissance of anticipated operating
areas. The Remote Mine-hunting System (RMS) is being developed to meet these requirements.
RMS will be an organic, off-board system employing advanced mine reconnaissance sensors that
will be launched, operated, and recovered from a host surface ship. RMS development will
continue to follow an evolutionary acquisition process in which upgraded systems are delivered to
the Fleet as the technology matures.
Program Status: In FY 1997, the RMS concept was successfully demonstrated by employment of a prototype system from the USS Cushing (DD-985) during an Arabian Gulf exercise. The Engineering and Manufacturing Development phase for RMS began in early FY 1998. The
operational system will be installed in the Arleigh Burke (DDG-51) Flight IIA Aegis guided missile
cruisers beginning with DDG-91 in FY 2003.
Developer/Manufacturer: Lockheed Martin, Syracuse, New York.
UUVs
Unmanned Underwater Vehicles
Description: The Navy’s first priority in its Unmanned Undersea Vehicle (UUV) plan is the rapid development of a covert mine reconnaissance capability. The Near-Term Mine Reconnaissance
System (NMRS) is being developed to meet this pressing requirement. NMRS will maximize the
use of existing Commercial Off-The-Shelf systems in a vehicle capable of launch and recovery
from the torpedo tubes of Los Angeles (SSN-688)-class submarines. NMRS will integrate
forward-looking sonar for obstacle avoidance and initial search capability with an improved
AN/AQS-14 side scan sonar for target classification. The Long-Term Mine Reconnaissance
System (LMRS) is in development to enter service in FY 2003 and provide a robust, long-term
capability to conduct clandestine minefield reconnaissance. The LMRS will replace the NMRS
and will provide a significantly improved capability, including submarine launch and recovery as
well as autonomous operation endurance of more than 40 hours.
Program Status: The NMRS operational prototype is scheduled for delivery in FY 1999.
Developer/Manufacturer: NMRS: Northrop Grumman, Annapolis, Maryland. LMRS: Northrop Grumman is preparing detailed designs for the production of LMRS.


 Return to the Table of Contents
Return to the Table of Contents








