ALE-47
Countermeasures Dispenser System
ALE-50 AAED
Advanced Airborne Expendable Decoy
 countermeasures against semi-active radar-guided anti-aircraft threats, thereby increasing the survivability of tactical
aircraft. The AN/ALE-50 decoy is deployed when required and cut free before landing.
countermeasures against semi-active radar-guided anti-aircraft threats, thereby increasing the survivability of tactical
aircraft. The AN/ALE-50 decoy is deployed when required and cut free before landing.
ALR-67(V)3
Advanced Special Receiver
APG-65
F/A-18 Hornet Radar Upgrade

ATARS
Advanced Tactical Air Reconnaissance System
AVR-2
Laser Warning System
Subsurface Systems
ADS
Advanced Deployable System
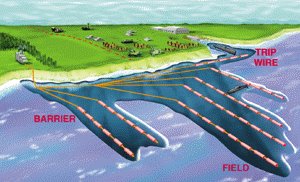
BLQ-10 ESM System
Virginia Class Electronic Support Measures

BQQ-10 A-RCI
Acoustic Rapid COTS Insertion

BSY-2
Submarine Combat System
CCS
Submarine Combat Control System
FDS-C
Fixed Distributed System-COTS
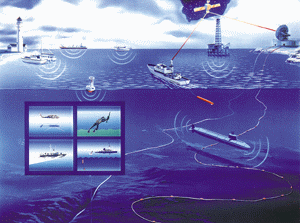
SOSUS
Sound Surveillance System
TB-29
Submarine Thin-line Towed Array
Surface Systems
AIEWS
Advanced Integrated Electronic Warfare System
Combat DF
Combat Direction Finding

IPDS CBR Defense
Improved Point Detector System
IRST
Infrared Search and Track
MFR
Multi-Function Radar
Nulka
Decoy System

SALAD CBR Defense
Shipboard Automatic Liquid Agent Detector
SLQ-32A
Electronic Warfare System

SPQ-9B
Radar Improvement Program
SPY-1
Aegis Multi-function Phased Array Radar

SQQ-89
Anti-Submarine Warfare Combat System
- AN/SQS-53C/D active/passive hull-mounted sonars (SQS-56 in FFGs)
- SQR-19 Tactical Towed Array System (TACTAS)
- Mk 116 ASW fire control system
- AN/SQQ-28 sonobuoy processor
- AN/SRQ-4 SH-60B helicopter data link
- AN/UYQ-25B Sonar In-situ Mode Assessment System (SIMAS)
- AN/USQ-132 Tactical Display Support System (TDSS)
- AN/SQQ-89( )-T On-Board Trainer (OBT)
- SH-60R (LAMPS Mk III Block II) integration
- Multi-Function Towed Array (MFTA) that will provide low and mid-frequency bi/multi-static capability between the SQS-53C/D, the SH-60R Airborne Low-Frequency Active Sonar (ALFS), and off-board systems
- Remote Mine-hunting System (RMS) processing and display
- Echo Tracker Classifier (ETC) active classification capability
- Computer-Aided Dead-Reckoning Table (CADRT)
- Torpedo Recognition and Alertment Functional Segment (TRAFS)
- Launched Expendable Acoustic Decoy (LEAD) to provide torpedo defense capability
TISS
Thermal Imaging Sensor System
ULQ-20 BGPHES-ST
Battle Group Passive Horizon Extension System-Surface Terminal
UQQ-2 SURTASS/Twin-Line Array
Surveillance Towed Array Sensor System
UQQ-2 SURTASS/LFA/T-AGOS-23
Surveillance Towed Array Sensor System,
Low Frequency Active


