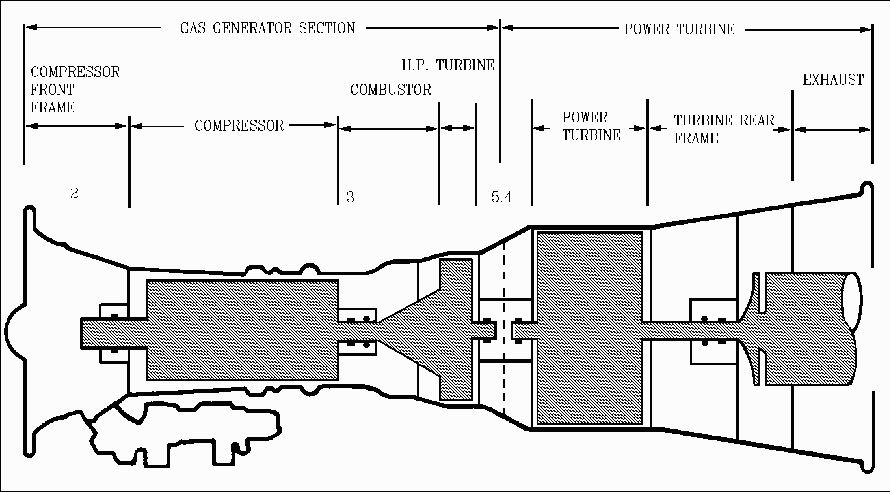
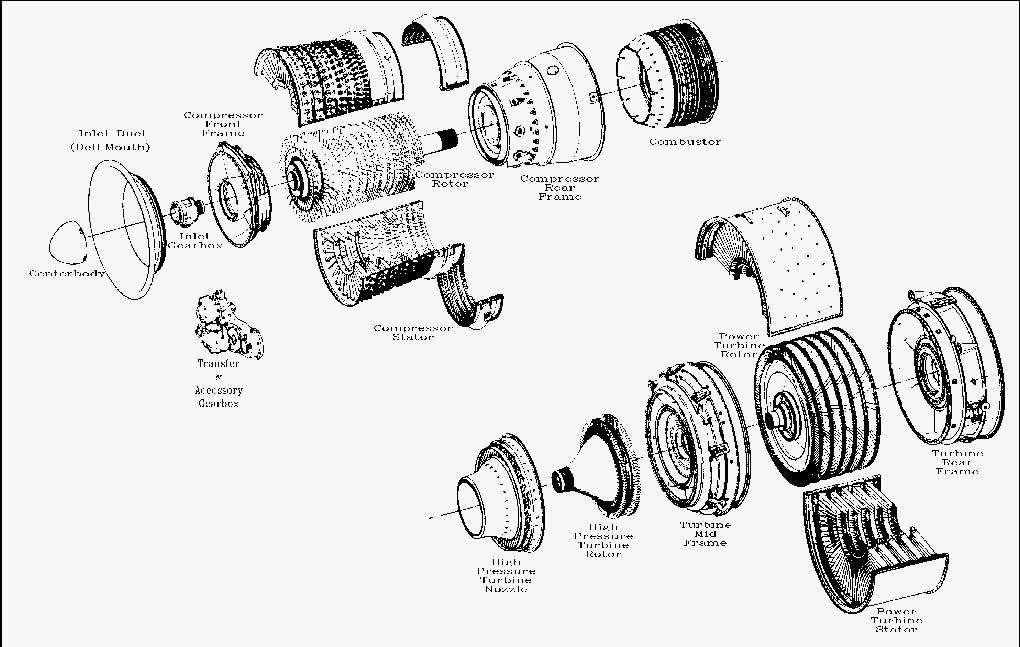


The LM2500 gas turbines drives controllable pitch propellers through a conventional main reduction gear, shaft and clutch. A 16 stage axial flow (air travel is parallel to the shaft) compressor increases the pressure and temperature of the working mass (air). In the combustor section, fuel is added through fuel nozzles and combustion occurs. A two stage high pressure turbine on the exhaust end of the combustor drives the compressor. The combination of the compressor, combustor, and high pressure turbine are often called the gas generator. The exhaust from the high pressure turbine passes through a low pressure turbine which extracts the work required to drive the main reduction gear and ultimately the ship's propeller. The LM2500 module totally encloses the LM2500 to provide thermal and acoustic insulation. A top hatch and a side door (DD/DDG/CG) or two side doors (FFG) provide access to and viewing of the engine. The module is shock mounted to reduce hull-borne noise transmission.
LM2500 Gas Turbine Engine has a 16 stage axial flow compressor made up of a 16 stage Compressor rotor of moving blades driven by the high pressure turbine. The Compressor stator casing contains one stage of Inlet Guide Vanes (IGV), six stages of Variable Stator Vanes (VSV) and 10 stages of stationary stator vanes. The IGVs and stator vanes 1-6 are variable, meaning they are variable geometry. The angle of attack of the blades can be changed to prevent compressor stall. Bleed air is extracted from the compressor for use in the ship's bleed air system and for internal use in the engine.
The combustor is an annular type with 30 fuel nozzles and 2 spark ignitors. Of the air from the compressor approximately 30% is mixed with fuel to support combustion. The other 70% is used to cool and center the flame within the combustion liner. The ignition system produces a high intensity spark to ignite the fuel/air mixture during the start sequence. Once the engine is started the ignitors are no longer needed and will be de-energized. High pressure turbine section extracts enough energy from the hot expanding gasses to drive the compressor and accessory drive. The HP turbine is a two stage axial flow type which is mechanically coupled to the compressor rotor. The HP turbine uses approximately 65% of the thermal energy from the combustor to drive the compressor and engine mounted accessories.The accessory drive assembly is driven through the compressor rotor shaft via the inlet gearbox, radial drive shaft, and transfer gearbox. The Accessory gearbox provides mounting for the fuel pump, lube oil pump, air/oil separator, and pneumatic starter.
The power turbine is a six stage axial flow type turbine. The power turbine extracts the remaining 35% of useable energy and uses this to drive the main reduction gear. The power turbine drives the reduction gear through a high speed flexible coupling shaft and clutch assembly. The high speed flexible coupling absorbs the radial and axial misalignment between the GTM and the main reduction gear. Foriegn Object Damage (FOD) is a major concern of gas turbine engines. FOD is simply debris of one form or other which can damage the internal components of a gas turbine engine. Propulsion and electrical generation turbines are no different than aircraft engines and the hazard FOD represents to the operation of these engines demands the attention of all personnel. On a flight deck periodic "FOD Walkdowns" keep the operating areas clear of debris. For shipboard engines FOD screens, wire mesh moisture separators, and if operating in a high air particulate environment "Scott" foam pads are used to filter incoming air and keep the engine operating.An advantage of a gas turbine engine is its ability to be removed from the ship for repair in a short period of time (approximately 72 hours). A set of rails is permanently installed in the intakes of each engine and a set of temporarily installed transition rails allow the disconnected engine to transit from its mounting attachments in the module onto the rails in the intakes. Crane service capable of extending over the soft patches in the intakes is required to pull the engine up the rails and out of the ship.

