




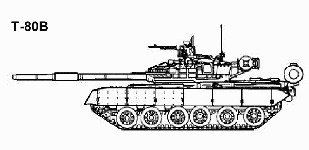
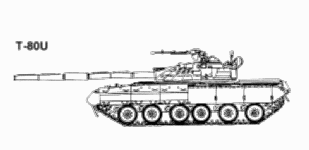



The T-80, manufactured by Transmash of Omsk, appeared as production model in 1984, retaining the basic features of the T-64 series (including the 125mm smoothbore gun with autoloader). Major innovations included the first Soviet use of a gas turnine engine, providing increased speed and power, and the first use of a laser rangefinder providing major improvements in fire control. The T-80 is very similar in appearance to the T-72. It incorporates features common to both the T-64 and T-72, especially in weaponry. Easily distinguishable features of this tank as compared with the standard T-72 are the attachment of side skirts and twelve turret-mounted grenade launchers with seven on the left side and five on the right side.
The T-80 was the first Soviet operational tank to be powered by a gas-turbines, with a GTD-1000 gas-turbine engine developing 1100 hp. The road wheel spacing is not identical, with distinct gaps between the three pairs of road wheels. To extend the operational range of the T-80, additional fuel tanks can be mounted at the hull rear, which can be quickly jettisoned if required. A large circular container mounted on the turret rear carries two snorkels for deep fording operations. The larger one provides an air intake for the gas-turbine, with the other being fitted onto the radiator grill. The T-80 was also the first production Soviet tank to incorporate a laser range finder and ballistic computer system. The original night sight is the II Buran-PA (800-1300 meters range). The 12.7-mm MG NSVT has both remote electronically operated sight PZU-5 and gun-mounted K10-T reflex sight. The night sight cannot be used to launch the ATGM. The daysight can be used at night for launching ATGMs if the target is illuminated. A variety of thermal sights is available, including the Russian Agava-2, French SAGEM-produced ALIS and Namut sight from Peleng. Thermal sights are available for installation which permit night launch of ATGMs. There are thermal sights available for installation which permit night launch of ATGMs.The T-80 uses the same 125-mm gun and horizontal ammunition system as the T-72, though the fire control system is an improvement over that fitted to earlier Soviet tanks. The BK-29 round, with a hard penetrator in the nose is designed for use against reactive armor, and as an MP round has fragmentation effects. The more recent BK-27 HEAT round offers a triple-shaped charge warhead and 50 mm more penetration. The electronic round fuzing system for Ainet rounds is available for other tanks. This round uses technology similar to that for French Oerlikon's AHEAD rouns. The round is specially designed to defeat targets by firing fragmentation patterns forward and radially, based on computer calculated settings from the laser range-finder and other inputs. Targets are helicopters and dug in or defilade priority ground threats, such as ATGM positions. Rate of fire is 4 rd/min. If the BK-29 HEAT-MP is used, it may substitute for Frag-HE (as with NATO countries) or complement Frag-HE. With three round natures (APFSDS-T, HEAT-MP, ATGMs) in the autoloader vs four, more antitank rounds would available for the higher rate of fire. The ATGM may be launched while moving slowly (NFI). The AT-8 can be auto-loaded with the two halves mated during ramming; but the stub charge is manually loaded.
When fitted with explosive reactive armor [ERA] the T-80 is virtually immune over its frontal arc to penetration from all current NATO ATGMs which rely on a HEAT warhead to penetrate armor. On the turret of the T-80, the panels are joined to form a shallow chevron pointing. Explosive reactive armor is also fitted to the forward part of the turret roof to provide protection against top attack weapons. The explosive reactive armor does not provide any added protection against APDS or APFSDS attack.
The challenge facing the Omsk factory is how to get its output onto the international market. Three weapons exhibitions held in Omsk produced minor results. But after participation in international displays in Adu Dabi in the Arab Emirates, Geneva, Cairo, Le Bourget in France and Farnborough in England the T-80U tank captured contracts from number of countries.
It is believed that China had ordered 200 T-80Us in late 1993.
As of late 1997 the well-publicized sale of 320 Ukrainian T-80UD MBTs to Pakistan appeared to be dead in the water. A total of only 35 T-80UDs had been delivered to Pakistan in two separate batches in March and May 1997. These 35 tanks were reportedly drawn from Ukrainian Army stocks and had capabilities below the level agreed to by the two countries. According to Moscow's Kommersant Daily, this apparently caused the Pakistani government to cancel the sale. The Russian government has been publicly against this sale from the very beginning, and has repeatedly refused to supply Ukraine with critical components needed to build the T-80UDs. While the more modern Ukrainian T-84 MBT is �80% Ukrainian-made,� the T-80UD is a largely Russian product. Pakistan had been assured by Ukraine that the contract for the T-80UDs would be honored in spite of pressure and lack of support from Russia. Without Russian support, its likely that the only T-80UDs to be seen in Pakistan will be those few already paraded through Islamabad.
Specifications | |
| Designations | T-80U SMT (Soviet Medium Tank) M1989 |
| Date of Introduction | 1987 |
| Current Using Countries | China Cyprus Pakistan Russia South Korea Ukraine |
| Description | |
| Crew | 3 |
| Combat Weight (mt) | 46.0 |
| Chassis Length Overall (m) | 7.01 |
| Height Overall (m) | 2.20 |
| Width Overall (m) | 3.60 |
| Ground Pressure (kg/cm 2 ) | 0.92 |
| Automotive Performance | |
| Engine Type | 1250-hp Gas turbine (multi-fuel), diesel on T-80UD |
| Cruising Range (km) | 335 km/600 km with extra tanks |
| Speed (km/h) | |
| Max Road | 70 |
| Max Off-Road | 48 |
| Average Cross-Country | 40 |
| Max Swim | N/A |
| Fording Depths (m) | 1.8 Unprepared, 5.0 w/snorkel, 12.0 with BROD-M system |
| Radio | R-173, R-174 intercom |
| Protection | |
| Armor, Turret Front (mm) | Against 120-mm ammunition |
| Applique Armor (mm) | Side of hull , over track skirt |
| Explosive Reactive Armor (mm) | Kontakt-5 2nd Generation ERA |
| Active Protective System | ARENA is available |
| Mineclearing Equipment | Roller-plow set and plows available |
| Self-Entrenching Blade | Yes |
| NBC Protection System | Yes |
| Smoke Equipment | Smoke grenade launchers (4x 81-mm each side of turret), and 24 grenades. Vehicle engine exhaust smoke system. |
| ARMAMENT | |
| Main Armaments | |
| Caliber, Type, Name | 125-mm smoothbore gun 2A46M-1 |
| Rate of Fire (rd/min) | 7-8 (lower in manual mode) |
| Loader Type | KORZINA separate-loading autoloader, and manual |
| Ready/Stowed Rounds | 28 in carousel/17 stowed (manual loaded) |
| Elevation (�) | -4 to +18 |
| Fire on Move | Yes (gun rounds and ATGMs) |
| Auxiliary Weapon | |
| Caliber, Type, Name | 7.62-mm (7.62x 54R) Machinegun PKT |
| Mount Type | Turret coaxial |
| Maximum Aimed Range (m) | 2,000 |
| Max Effective Range (m) | |
| Day | 800 |
| Night | 800 |
| Fire on Move | Yes |
| Rate of Fire (rd/min) | 250 practical / 650 cyclic, 2-10 round bursts |
| Caliber, Type, Name | 12.7-mm (12.7x108) AA MG NSVT |
| Mount Type | Turret top |
| Maximum Aimed Range (m) | 2,000 |
| Max Effective Range (m) | |
| Day | 1,500 |
| Night | 800-1,300 |
| Fire on Move | Yes |
| Rate of Fire (rd/min) | 210 practical/ 800 air targets in bursts |
| ATGM Launcher | |
| Name | 2A46M-1 tank gun |
| Launch Method | Gun-launched |
| Guidance | SACLOS, Laser-beam rider |
| Command Link | Encoded infrared laser-beam |
| Launcher Dismountable | No |
| FIRE CONTROL | |
| FCS Name | FCS 1A42 |
| Main Gun Stabilization | 2342, 2-plane |
| Rangefinder | Laser |
| Infrared Searchlight | Yes |
| Sights w/Magnification | |
| Gunner | |
| Day | 1G46/PERFECT, 3.6/12x |
| Field of View (�) | INA |
| Acquisition Range (m) | 5,000 (70%P-hit for ATGM) |
| Night | AGAVA-2 |
| Field of View (�) | INA |
| Acquisition Range (m) | 2,600 (gun rounds only) |
| Commander Fire Main Gun | Yes |
| MAIN ARMAMENT AMMUNITION | |
| Caliber, Type, Name | |
| 125-mm APFSDS-T, BM-42M | |
| Maximum Aimed Range (m) | 3,000-4,000 |
| Max Effective Range (m) | |
| Day | 2,000-3,000 |
| Night | 800-1,300 |
| Armor Penetration (mm) | 590-630 at 2,000 meters |
| 125-mm HE-Shapnel Focused-fragmentation, Ainet | |
| Maximum Aimed Range (m) | 5,000 |
| Max Effective Range (m) | |
| Day | 4,000 |
| Night | 800-1,300 |
| Tactical AA Range | 4,000-5,000 |
| Armor Penetration (mm) | INA |
| 125-mm Frag-HE-T, OF-26 | |
| Maximum Aimed Range (m) | 5,000 |
| Max Effective Range (m) | |
| Day | INA |
| Night | 800-1,300 |
| Armor Penetration (mm) | INA |
| 125-mm HEAT-MP, BK-29M | |
| Maximum Aimed Range (m) | 4,000 |
| Max Effective Range (m) | |
| Day | INA |
| Night | 800-1300 |
| Armor Penetration (mm) | 650-750 |
| 125-mm HEAT, BK-27 | |
| Maximum Aimed Range (m) | 4,000 |
| Max Effective Range (m) | |
| Day | INA |
| Night | 800-1,300 |
| Armor Penetration (mm) | 700-800 |
| Other Ammunition Types | Giat 125G1 APFSDS-T, Russian BM-42 and BM-32 APFSDS-T. The Russians may have a version of the BM-42M with a DU penetrator. |
| Antitank Guided Missiles | |
| Name | AT-11/SVIR |
| Warhead Type | Shaped charge (HEAT) |
| Armor Penetration (mm) | 700 (RHA) behind ERA/800 conventional |
| Range (m) | 5,000 |
| Name | AT-11B/INVAR |
| Warhead Type | Tandem shaped charge |
| Armor Penetration (mm) | 800 (RHA) behind ERA /870 conventional |
| Range (m) | 5,000 |






