




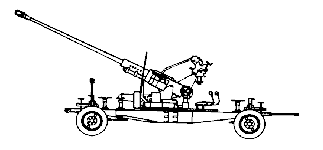




Recognition features of the S-60 are the long, thin tube with multi-perforated muzzle brake, distinctive gun shield which folds down and the horizontal feed tray which holds the four-round clips. The normal Soviet prime mover is the Ural-375 truck. The four-wheel carriage can be leveled and stabilized on jacks to form a point firing base. Loading is accomplished by 4-round horizontally fed clips. The S-60 also has an ammunition ready rack that can hold 4 four-round clips near ammunition feed mechanism on left side of the breech. A twin version, the S-68, is mounted on the self-propelled ZSU-57-2, and twin and quad versions are used by the Soviet Navy. It should be noted that the ammunition for the 57mm antiaircraft guns is not_ interchangeable with that used by the 57mm antitank and assault guns. This is due to the different configuration and dimensions of the cartridge cases. Besides on-carriage optical fire control, the S-60 also employs an off-carriage FLAP WHEEL fire control radar, mounted on a separate van.
The towed S-60 system lacks the mobility of the newer SAM systems with which it is being replaced. A self-propelled version, the ZSU-57-2, with twin 57-mm guns mounted on a modified T-54 tank chassis, was introduced in 1957. The ZSU-57-2 has the same characteristics as the S-60 except that it is not radar-controlled. It is now considered obsolete.
Tactical AA range is 4,000 meters with optical sights and 6,000 meters with radar guidance. This weapon, designed to provide defense against aircraft and helicopters, can also be used against lightly armored ground vehicles in a ground support role.The S-60 was found in the antiaircraft regiment of some motorized rifle and tank divisions to protect critical assets. However, by the 1980s it had been replaced in most Soviet divisions by the SA-6/GAINFUL or SA-8/GECKO SAM systems. It also may be found in territorial defense units, especially around airfields. An S-60-equipped regiment has 24 guns: four firing batteries each consisting of six guns and a fire control center. A S-60 battery will generally consist of six guns, a fire-control radar, and a fire-control director. Some versions may have the FLAP WHEEL as the primary fire control radar.
The S-60 was built by the Chinese [designated Type 59] and has seen combat in the Middle East. In Vietnam it was the keystone of North Vietnamese low-altitude air defense and was most effective between 460 meters (1,500 feet) and 1,500 meters (5,000 feet).
Specifications | |
| S-60 57MM Antiaircraft Gun | |
| Characteristics: | |
| Crew | 7 |
| Length | 8.5 m |
| Height | 2.37m |
| Width | 2.054m |
| Combat Weight | 4,660 kg |
| Armament: | |
| Antiaircraft gun | 57mm single barrel, traverses 360 degrees |
| Maximum effective range (vertical) | 6 km (radar guided); 4km optically guided |
| Rate of fire | Maximum: 105-120 rds/min cyclic Sustained: 70rds/min |
| Type of ammunition | API-T, HEI-T |
| Basic Load | INA |
| Fire Control | FLAP WHEEL radar,mounted on saparate van, and an optical-mechanical system |
| Vehicle: (prime mover) | URAL-375 general purpose cargo truck |
| Maximum road speed | 75km/hr (47 mph) |
| Water Crossing ability | Fords 1.5m (5 feet) |
| Cruising range (on roads) | 750 km (450 miles) |
| Night vision aids | Infrared system can be fitted |
| Maximum armor thickness | No armor |
| NBC Protection | None |
| Vulnerabilities: |
Fixed location |
| Exposed personnel | |
| Optics vulnerable to obscuration | |
| Exposed ammunition | |
| Exposed antennas | |
| Exposed, thin-skinned radar van | |
| Recognition: | |
| Long thin gun tube with multiperforated muzzle brake | |
| Four-wheeled carriage | |
| Large folding gun shield | |
| Wheels raised in firing position, but may be fired from the travelling position | |





