Su-25 FROGFOOT Grach (Rook)
Su-39 FROGFOOT
The Su-25, which is no longer in serial production, made its first flight in 1979. This single seat
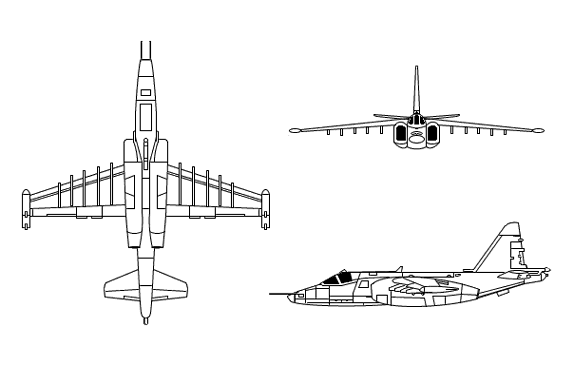
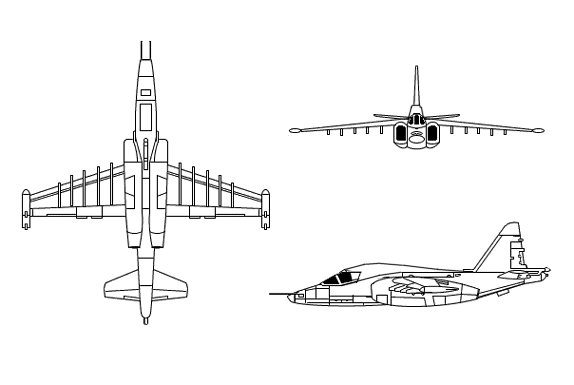
ground attack aircraft is a very durable airplane - it is fairly heavily armored -- and easy to service - all service equipment can be stored in a container and transported by the airplane itself. It is armed with one twin barrel 30mm gun in the bottom of the fuselage with 250 rounds. There are 8 pylons under the wings which can carry about 4,000 kg of air-to-ground weapons, including 57mm to 330mm rockets. There are two small outboard pylons for AA-2D/ATOLL or AA-8/APHID AAMs.
The wings are high-mounted and back-tapered with straight trailing edges. There are pods mounted at the square tips. There are two turbojets mounted alongside the body under the wings. There are semicircular air intakes forward of the wings� leading edges. There are exhausts to the rear of the wings� trailing edges. The fuselage is long, and slender and has a rounded nose. The body tapers to the rear section that overhangs the exhausts. There is a stepped canopy. The tail is swept-back and fin is tapered with a square tip. The flats mid-mounted on the fuselage, unequally tapered with blunt tips.
The Su-39 (also known as the Su-25T or Su-25TM) is a Frogfoot variant incorporating post-Afghanistan lessons-learned. It is based on the Su-25UB two-seat trainder, with the rear seat and cockpit replaced with a fuel cell and extra avionics. The Su-39 carries the Kopyo-25 multi mode radar in a pod under the fuselage. Armament includes ground attack missiles such as the AT-16 Vikhr , anti-ship missiles, and AAMs such as the R-27, R-27ER, R-60, R-73 and R-77. A four-fold reduction in thermal signature has been achieved through cooling intakes on the upper surface of aircraft, and a new center body which masks hot turbine blades. Only a few dozen of these aircraft have been built. Reports in the mid-1990s that the Su-39 designation had been assigned to a primary trainer derived from the Su-26 and Su-29 aerobatic competition aircraft, designed to replace the Yak-52, are apparently incorrect.
VARIANTS
- Su-25 (Frogfoot A) -- Original production ground attack aircraft with R-95 engines
- Su-25K -- Export version of Su-25
- Su-25UB (Frogfoot B) (UB - Uchebno-Boevoi, Combat Trainer) -- Two-seat combat trainer
- Su-25UBK -- Export version of Su-25UB
- Su-25UBP -- Naval trainer based on Su-25UB
- Su-25UT (Frogfoot B) (UT - Uchebno-Trenirovochnyi, Trainer) -- Unarmed primary trainer (sometimes referred to as Su-28)
- Su-25UTG (Frogfoot B) (UTG - Uchebno-Trenirovochnyi Gakovyi, Trainer Naval) -- Naval trainer based on Su-25UT
- Su-25BM -- Enhanced ground attack aircraft with R-195 engines, this is the current production version, and the most numerous in Russian service
- Su-25T (Su-25TM Tankovyi Modifitsirovannyi, Antitank) -- Proposed enhanced version with more armour, improved sensors, and possibly a new gun and engines [Su-25T's production designation is Su-39]
- Su-25TK -- Proposed export version of Su-25T
Specifications | ||
| Country of Origin | ||
| Builder | SUKHOI | |
| Similar Aircraft | | |
| Crew | One | |
| Role | | |
| VARIANT | Su-25 | Su-39 |
| Length | 47 ft, 6 in (14.6 m) | 14.52 m |
| Span | 50 ft, 10 in (15.6 m) | 15.33 m |
| Engines | 2x Tumanski R-195 @ 44,1 kN | |
| Weight | 17,600kg (loaded) | 21500 kg |
| Maximum Speed | .8 Mach | 950 km/h |
| Maximum Ceiling | 7000 meters | 10000 meters |
| Service Ceiling | 7000 meters | |
| Maximum Range | Unknown | 2500 km |
| Cruise range | 750nm | 650 - 900 km |
| Combat Range | 1,250 km (with drop tanks) | |
| In-Flight Refueling | No | |
| Internal Fuel | 3500 kg | |
| Payload | 4400 kg | 6000 kg |
| Sensors | RWR, laser designator, LRMTS | |
| Drop Tanks | 600 L drop tank 479kg for 51nm range | |
| Armament | Cannon: 1 GSh-6-N-30 30mm rotary AS-7/9/11/12, AA-8 Aphid, FAB-250, UV-32-57, FAB-500, 500kg LGB, FAB-250 |
|
| User Countries |
| Russia |
Su-25



















Su-39

Sources and Resources
- Su-25 (Su-28) Frogfoot Close-Support Aircraft, Air Force Technology



