FAS |
Military |
DOD 101 |
Systems |
Aircraft |
ROW ||||
Index |
Search |
Join FAS




Kfir
F-21A
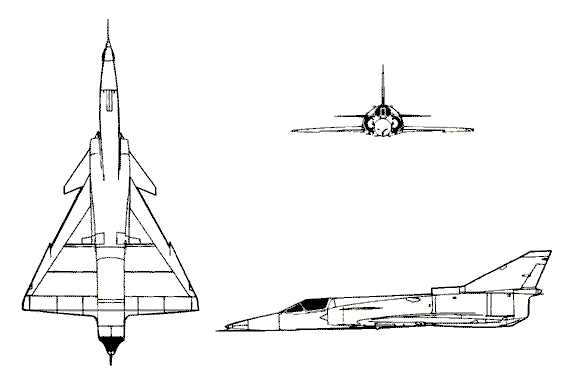
The Kfir (which means lion cub) is basically a redesigned Mirage 5 with a canard mounted on the air intake. The wings are low-mounted, delta-shaped with a sawtooth in the leading edges. There are small canards are mounted on the air intakes. There is one turbojet engine inside fuselage. There are semicircular air intakes alongside the fuselage. There is a large, single exhaust. The fuselage is tube-shaped with a long, solid, pointed nose. The body widens at the air intakes. There is a bubble canopy flush with the spine. The tail has no tail flats. The fin is swept-back and tapered with a prominent step in the leading edge.First flown in June 1973, the Kfir-C1 was in essence the airframe of the Dassault-Breguet Mirage III/5 series mated to the General Electric J79 afterburning turbojet and fitted with a suite of Israeli electronics. The type was designed after the manufacturer had gained experience with the Nesher (eagle), which was an unlicensed copy of the Mirage IIICJ with an equally unlicensed Atar turbojet, produced mainly for Israeli service but later exported as the Dagger. The Kfir-C1 entered only limited production (27 aircraft), with two squadrons equipped from 1974 pending the introduction of more advanced derivatives.
Kfir-C1 fighters with small canards but no armament were delivered to the US Navy and Marine Corps with the designation F-21A for use as "aggressor" aircraft in dissimilar air combat training.
The Kfir-C2, introduced in 1976 after a first flight in 1974, was a developed version of the Kfir-C2 designed to keep the type viable against all conceivable threats well into the 1990s. The result is a warplane with formidable combat capabilities plus short-field performance thanks to the sustained manoeuvrability and control effectiveness resulting from the aerodynamic developments. The type is distinguisable from the Kfir-C1 by its dogtoothed outer wing panels, small undernose strakes and, most importantly of all, swept delta canard foreplanes.
The Kfir-C7, the definitive single-seat version introduced in 1983, is based on the Kfir-C2 with a specially adapted version of the J79-GEJ1E with some 1,000 lb (454 kg) more afterburning thrust. The type has two extra hardpoints and a number of advanced features including capability for the carriage and use of 'smart' weapons, Elta EL/M-2021B pulse-Dopplar radar, a revised cockpit with more sophisticated electronics and HOTAS (Hands On Throttel And Stick) controls and provision for inflight-refueling. Maximum take-off weight is increased by 3,395 lb (1,540 kg), but combat radius and (more importantly) thrust-to-weight ratio are improved to a marked degree.
Specifications | |
| Country of Origin | Israel |
| Constructor | Israel Aircraft Industries (IAI) |
| Similar Aircraft | |
| Crew | |
| Role | |
| Armament | 13,415 lb (6,085 kg) of mixed ordinances |
| Length | 53 ft, 8 in (16.36 m) |
| Span | 27 ft (8.24 m) |
| Speed | Mach 2.3 |
| Combat Radius | 768 KM |
| Range | 2,008 miles (1744 nautical miles |
| User Countries | |
Sources and Resources
FAS |
Military |
DOD 101 |
Systems |
Aircraft |
ROW ||||
Index |
Search |
Join FAS
http://www.fas.org/man/dod-101/sys/ac/row/kfir.htm
Maintained by Robert Sherman
Originally created by John Pike
Updated Thursday, March 11, 1999 7:47:49 PM



