

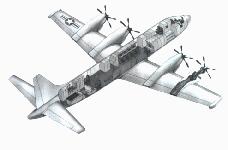



The P-7 Long Range Air ASW-Capable Aircraft (LRAACA) was intended to replace the P-3 Orion as the primary land-based ASW patrol aircraft. The Navy selected Lockheed in October 1988 to develop this next generation maritime patrol aircraft, a virtually a new design derived from the P-3C.
In the mid-1980s, the Navy initiated efforts to replace the large number of P-3 aircraft estimated to reach the end of their useful service lives during the 1990s. Over the years, the P-3C, the Navy's latest model P-3aircraft, has lost some of its range and time on station capabilities because of heavier required payloads. The Navy sought a replacement plane with increased payload. and at least the original P-3C range. The Navy also sought an aircraft with newer technology that could reduce support costs and provide enhanced antisubmarine warfare capabilities.
The envisioned aircraft was a derivative of the P-3C and became known as the P-3G. It was to include improved engines, reliability, maintain-ability, and survivability enhancements, vulnerability reductions, andadvanced mission avionics. The Navy planned to acquire 125 P-3G air-craft over a 5-year period. The Navy had been buying various versions of the P-3 from Lockheed without competition for many years, and it believed that introducing competition into further procurement would result in cost savings. The Navy sent a request for information to industry in May 1986. Using information obtained from the respondents, the Navy developed a P-3G specification that met its operational requirements. In August 1986, Office of the Secretary of Defense officials approved the P-3G program.
In January 1987, the Navy released a draft request for proposal (RFP) for the P-3G. Following release of the draft RFP, no company other than Lockheed indicated an interest in building a P-3C derivative. Unwilling to award a contract to Lockheed without competition, the Navy expanded the scope of competition in March 1987 to include modified commercial aircraft as well as aircraft based on the P-3C design.
In May 1987, OSD directed the Navy to conduct a patrol aircraft mission requirements determination study (payload, range, speed, survivability,etc.). To complement this study and enhance the RFP, the Navy released a draft RFP to industry soliciting comments on the operational potential of commercial derivative aircraft to perform the patrol aircraft mission. In September 1987, the Navy released a final RFP, incorporating the findings of the OSD-directed study and the responses from industry.
Three proposals were received and evaluation began in February 1988. In October 1988, the Navy selected Lockheed as the winner of the competition. Lockheed's proposal was significantly lower in cost than proposals submitted by Boeing and McDonnell Douglas. It was also judged to be technically superior, with a less risky technical approach.
On January 4, 1989, the Defense Acquisition Board,(DAB) recommended full-scale development of the program. The next day, the Navy awarded a fixed-price incentive contract to Lockheed to design, develop, fabricate, assemble, and test two prototype aircraft, designated the P-7A. The contract had a target cost of $600 million and a ceiling price of about $750 million. In March 1989, the Navy estimated acquisition of 125 P-7A aircraft at about $7.9 billion (escalated dollars). Of this total, development cost was estimated at $915 million (escalated dollars). Procurement of each production version aircraft was estimated at about $56.7 million.
In November 1989, Lockheed announced a $300-million cost overrun in its development contract due primarily to schedule and design problems. In the following months, Navy and Lockheed officials held extensive but unsuccessful discussions in an attempt to address the contract issues. By letter dated July 20, 1990, the Navy terminated the P-7A development contract for default, citing Lockheed's inability to make adequate progress toward completion of all contract phases.
The bulk of funds in the amended FY1991 budget request for the P-3 modernization program were for the P-7 LRAACA aircraft program. Continuation of the P-7A contract was one option that was presented to the Defense Acquisition Board (DAB) in November 1990. Both the House and the Senate fully funded the request. In order to avoid prejudicing the DAB decision process, the Congress decided to authorize an amount that would fully fund the fiscal year 1991 effort of any of the alternatives to be considered by the DAB.
The program was finally cancelled by the DAB at the end of 1990, on the grounds that it had fallen behind schedule, which called for the two prototypes to be delivered in 1992. Some 123 production P-7As had been planned. This decision left the Navy without a program to replace its aging P-3 aircraft. The Boeing Update IV avionics upgrade, an important element of the P-7A, was initially to have been applied to 109 earlier US Navy P-3Cs, but in 1992 this work was also cancelled.
The British Nimrod MR2P was to have been replaced by the P-7A, but cancellation of that program forced the British Ministry of Defence to issue requirement SR(A)420 for a replacement maritime patrol aircraft (RMPA).




Specifications | ||
| P-3C | P-7A | |
| Max Takeoff Gross Weight | 139,760 lbs | 171,350 lbs |
| Flight Design Gross Weight (3.0g) | 135,000 lbs | 165,000 lbs |
| Maneuver Weight (3.5g) | 137,000 lbs | |
| Design Zero Fuel Weight | 77,200 lbs | 105,000 lbs |
| Maximum Payload | 22,237 lbs | 38,385 lbs |
| Fuel Capacity | 62,587 lbs | 66,350 lbs |
| Maximum Landing Weight | 114,000 lbs | 144,000 lbs |
| Design Landing Weight | 103,880 lbs | 125,190 lbs |
| Sonouoy Capacity | 84 | 150-300 |
| Wing Span | 99.6 ft | 106.6 ft |
| Wing Area | 1300 sq ft | 1438 sq ft |
| Fuselage Length | 116.8 ft | 112.7 ft |
| Height | 34.2 ft | 32.9 ft |