 Engineering Training
Engineering Training Engineering Training
Engineering TrainingASSIGNMENT SHEET
AMPHIB/AUXILIARY SYSTEMS
Assignment Sheet Number 62B-402
INTRODUCTION
As an Engineering Officer aboard a ship with amphibious capability you may be frequently tasked to provide support directly affecting ship’s mission. Auxiliaries Division may be the primary provider of maintenance and operational expertise in well deck and ballasting equipment operations.
The stern gate is attached to the stern of the ship at the waterline. When closed, it acts as a seal which prevents water from entering the deck area. When opened the gate is a stable launching ramp for on-loading and off-loading troops, boats, and amphibious craft. A turntable is a circular, flat rotating steel structure used to rotate vehicles allowing them to change direction in a limited space. The turntable allows for less operational running time of the vehicle and its subsequent exhaust fumes. Well deck ventilation ensures that fumes exhausted from equipment can be controlled and removed to safeguard personnel from exposure. The portable ramp and fixed ramps allow for vehicles to enter and leave the well deck, turntable, boat deck and flight deck. The water barrier provides for a part of the well deck to be dry while the rest of it can be flooded for well deck operations. The ability to control buoyancy optimizes list, draft, and trim by filling/emptying ballast tanks or transferring fuel oil through the ballasting/deballasting system.
LESSON TOPIC LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Terminal Objective:
11.0 DESCRIBE the function, theory of operation, operating parameters, design characteristics and maintenance requirements of shipboard auxiliary systems and support equipment.
Enabling Objective:
11.28 DESCRIBE the function and operation of the stern gate components:
a. Winch
b. Motor
c. Brakes (manual and electric)
d. Winch rigging
e. Control stations
f. Gate locking devices (deployed and secured)
g. Proximity switches
h. Audible alarms
11.29 DESCRIBE the construction, function, and operation of the following turntable components:
a. Turntable structure
b. Locking devices
c. Motor
d. Drive train
e. Brakes (manual and electric)
f. Clutch
g. Emergency hand drive mechanism
h. Audible alarms
I. Operational safety precautions
j. Control stations
11.30 DESCRIBE the construction, function, and operation of the following tank/well deck ventilation system components:
a. Ventilation fans
b. Natural ventilation accesses
c. Control stations
11.31 DESCRIBE the construction, function, and operation of the following ballast system components:
a. Ballast tank
b. Ballast pump
c. Ballast control console
d. Tank level indicators
e. Sounding tubes
f. Hydraulic control stations
g. Air deballast compressors
h. Air deballast control unit
i. Silencer
j. Filter
k. Blow/vent valve
l. Drain valve
m. Deballast valve
n. Fill valve
11.32 DESCRIBE the ballast, deballast, and stripping system.
11.33 DESCRIBE the effects on ship stability when conducting refueling, fuel oil transfer, ballasting, and stripping evolutions.
11.34 STATE the information available on the flooding effects and liquid loading DC diagrams.
11.35 UNASSIGNED; reserved for future use.
11.36 UNASSIGNED; reserved for future use.
11.37 UNASSIGNED; reserved for future use.
STUDY ASSIGNMENT
STUDY QUESTIONS
STUDY SCENARIO
The ship is currently conducting a beach landing with a full embarkation of marines and equipment. You are the Auxiliaries Officer. You have been discussing debarking with a Marine Captain when all power is lost in the aft end of the ship.
How does the complete loss of power affect auxiliary equipment that supports ops?
INFORMATION SHEET
AMPHIBIOUS SHIP OPERATION
Information Sheet Number 62B-402
INTRODUCTION
As an Engineering Officer aboard a ship with amphibious capability you may be frequently tasked to provide support directly affecting ship’s mission. Auxiliaries Division may be the primary provider of maintenance and operational expertise in well deck and ballasting equipment operations.
The stern gate is attached to the stern of the ship at the waterline. When closed, it acts as a seal which prevents water from entering the deck area. When opened the gate is a stable launching ramp for on-loading and off-loading troops, boats, and amphibious craft. A turntable is a circular, flat rotating steel structure used to rotate vehicles allowing them to change direction in a limited space. The turntable allows for less operational running time of the vehicle and its subsequent exhaust fumes. Well deck ventilation ensures that fumes exhausted from equipment can be controlled and removed to safeguard personnel from exposure. The portable ramp and fixed ramps allow for vehicles to enter and leave the well deck, turntable, boat deck and flight deck. The water barrier provides for a part of the well deck to be dry while the rest of it can be flooded for well deck operations. The ability to control buoyancy optimizes list, draft, and trim by filling/emptying ballast tanks or transferring fuel oil through the ballasting/deballasting system.
REFERENCES
(a) 0905-LP-060-2010, Hull and Mechanical, Volume 1
(b) S9LSD-BH-SIB-020, Machinery Plant, Volume 2
(c) NSTM Chapter 584, Stern Gates, Ramps, Bow Doors, Turntables, and Water Barriers
(d) 9SLSD-HB-SIB-020, LSD-41 SIB
(e) S9584-AH-MMA-010, Vehicle Turntable and Operating Gear (LSD)
(f) NSTM Chapter 584, Stern Gates, Ramps, Bow Doors, Turntables, and Water Barriers
(g) NSTM Chapter 510, Ventilation, Heating, Cooling and Air Conditioning Systems
INFORMATION
Stern Gate- Figure 1
Stern Gate Machinery Room- Figure 2
Vehicle Turntable- Figure 3
Carbon monoxide exhaust/safe exposure time guide for personnel |
|
Number of operating vehicles |
Maximum exposure time for personnel |
1 to 2 |
8 hours |
3 to 6 |
1 hour |
7 to 12 |
1/2 hour |
13 to 24 |
1/4 hour |
Note: Under no circumstance is the vehicle-time relationship to be exceeded. Only personnel required for vehicle operation should be in the vehicle stowage well when the vehicles are operating.
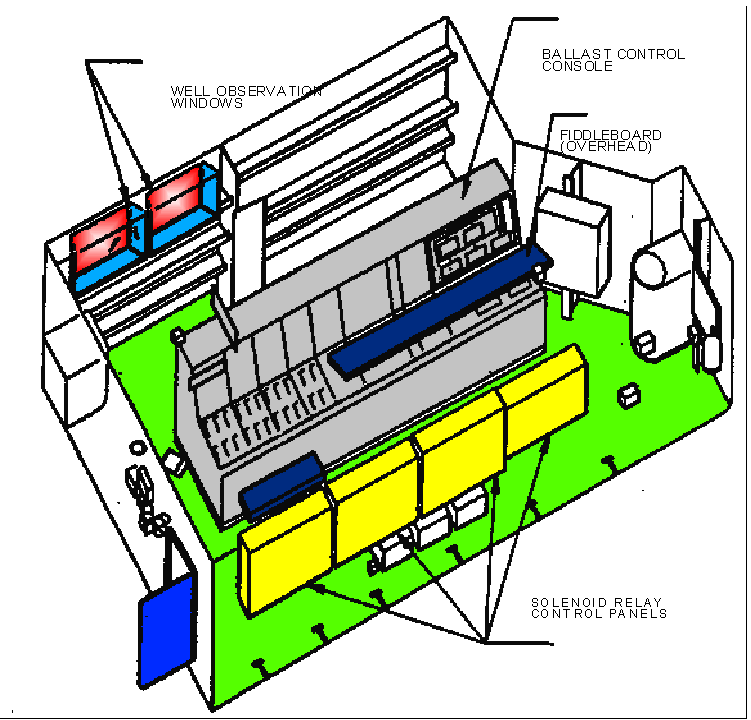
Ballast Control Console - Figure 4
Ballast tank (below water line) - Figure 5