



Naval Station Pascagoula
Pascagoula, Mississippi
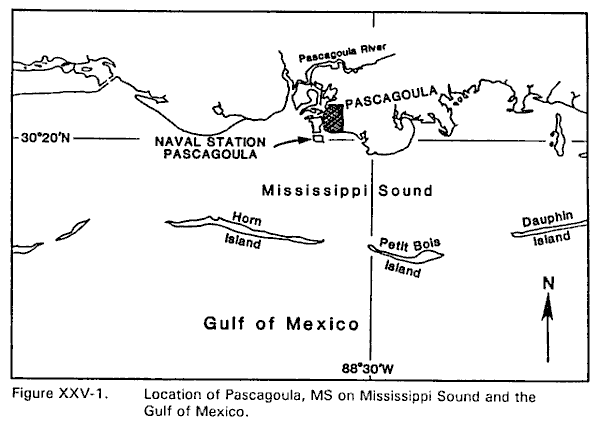
Naval Station Pascagoula, Mississippi is located on the mainland side of Mississippi Sound at approximately 30�20'N 88�35'W in the northeast portion of the Gulf of Mexico. The Port of Pascagoula is an important deep water port in the Gulf region.
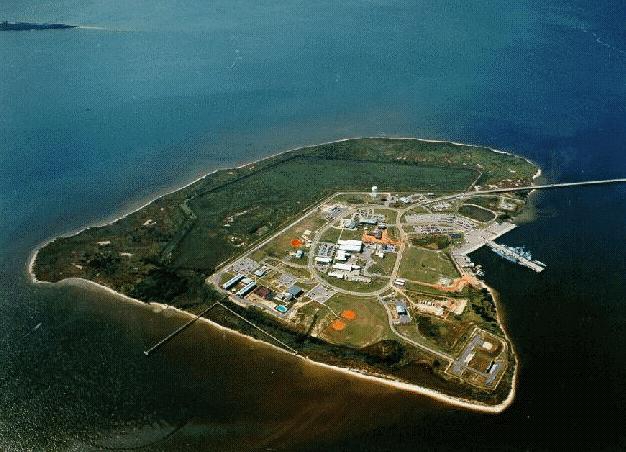
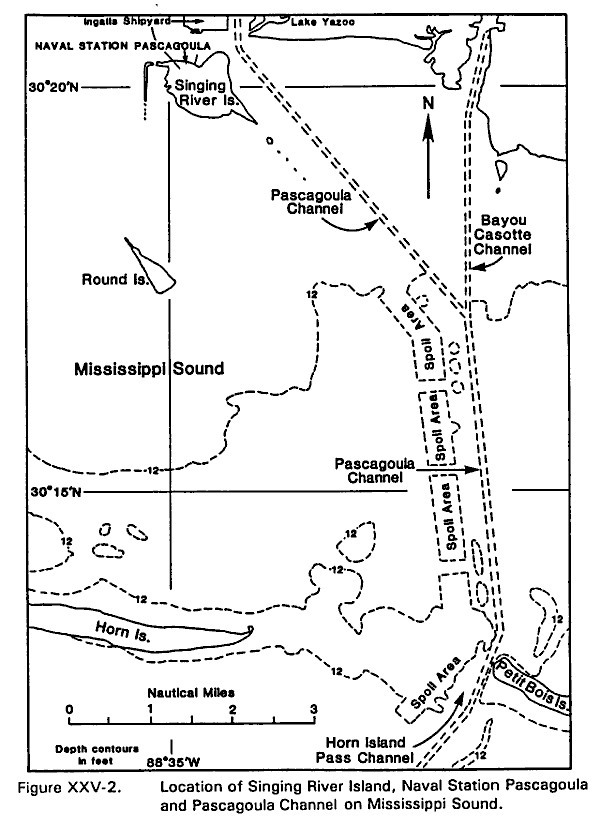
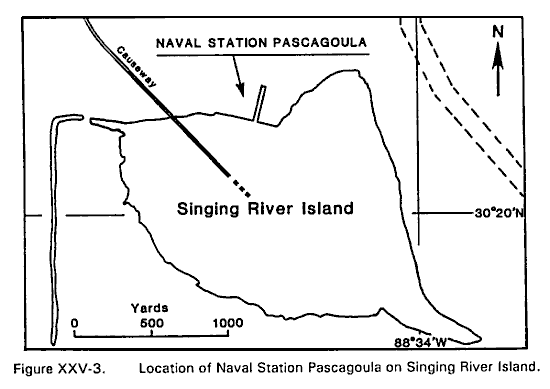
Naval Station Pascagoula is located on the north side of small, man-made Singing River Island. The island is situated just south of Ingalls Shipyard and southwest of the main port at Pascagoula. Access to the port from the open Gulf is gained via the Horn Island Pass Channel. The channel passes through dredged cuts between the extreme eastern limit of the water area between the east end of Horn Island and the western end of Petit Bois Island. From there the 350-ft wide channel proceeds
north and northwest, as Pascagoula Channel, about 9 nmi to Pascagoula and the Naval Station. The federal project depth of the channel is 40 ft in the Horn Island Pass Channel, and 38 ft in Mississippi Sound . However, Department of Commerce Chart 11373, 31st edition dated October 24,
1987 lists controlling depths from seaward in Pascagoula channel as 30 ft in the left outside quarter of the channel to 34.4 ft in the right outside quarter. Channel depth from the main ship channel to the Naval station is not specified. Outside the channel, Mississippi Sound is relatively shallow at the south end, ranging from 12 to 20 ft, and very shallow, as little as 2 to 4 ft, at the north end near Pascagoula. The land on which the Naval Station is constructed is only about 2 or 3 ft above sea
level. The surrounding terrain is also low in elevation. The only access to/from Singing River Island and the mainland is via a 14 ft high, 3-mile long causeway.
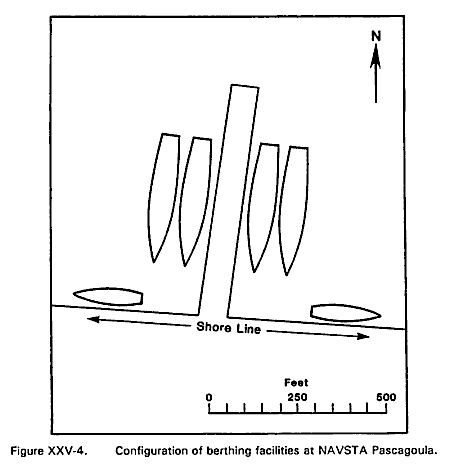
The Naval Station has a single pier which extends north-northeastward from the north side of Singing River Island. The pier, with a length of 680 ft. and a width of 80 ft. has two levels. Ship services are available from the lower level. Nesting will be required if more than two of the frigates assigned to Naval Station Pascagoula are in port at the same time. Additional moorage space for smaller vessels is provided at the quays along the shore at the south end of the pier.
Weather permitting, deep draft vessels may anchor 1 to 2 miles south or southeast of the sea buoy. Anchorage for vessels with up
to 15 ft draft is available in Mississippi Sound east of the channel.
The Port of Pascagoula is equipped with extensive large and small ship repair facilities. Ingalls Shipbuilding Corporation has a floating drydock with a depth of 41 feet over the keel blocks, a lifting capacity of 38,000 tons, and can handle vessels up to 820 ft long and 170 ft wide. It also has a graving dock 485 ft long and 85 ft wide, with a depth of
35.8 ft over the keel blocks. Other facilities include cranes with up to 60-ton capacities at the outfitting piers, floating cranes, and tugs with up to 4,200 hp.
The hurricane season poses a serious threat to Naval Station
Pascagoula. During the 107-year period from 1886-1992, an average
of one tropical cyclone or hurricane has passed within 180 nmi of
Pascagoula each year. The area is susceptible to storm surge, with
water elevations of over 6 ft being recorded four times during the
period of 1909 through 1969.

Sources and Methods
http://www.fas.org/man/dod-101/fac/port/pascagoula.htm
Maintained by Robert Sherman
Originally created by John Pike
Updated Sunday, December 06, 1998 5:59:17 AM












